Instagram is one of the well-known Social media platforms on the Internet where Reliable personalities have created their account, and they used to be active on it every day.
On the other hand, if we talk about Facebook, it used to be a platform that many people would have used in the past. But now, some fewer people used to spend time on it. The major reason behind this is the traffic of fake people and irrelevant activities that has made this platform quite boring.
Instagram is one outstanding place where every single person is enjoying their time. Since it’s a highly-traffic generated platform, many celebrities or famous personalities used to host Giveaways on this platform for their fans.
If you have just become famous on Instagram and plan to host the first giveaway, you need to read the whole article. We will be sharing much fruitful information on this article to provide you with benefits that you have never thought of before.
Also Read: (Instagram Stories) Share with Only Close Friends
In general, we will be talking about the Free Instagram comment Picker and Giveaways Tool. You would have been heard about it in the past time as well.
First, however, we will talk about the one that is ideal for you to use in the current time with various options. Yes, you can use the Free Instagram Comment Picker without login details, which we will be talking about here.
So, let’s start talking about the best Free Instagram Comment Picker Online and how you can use them.
Comment-Picker
Comment-Picker is a free online platform where you can get a Result for the Giveaway based on Selecting the Winners with the help of comments made on to the post. With this platform, you can take the help of Mentions, Tags, or various other options to find out the winner.
It would be effective for anyone to consider this option for a person who has been running the Giveaways for a long time, or it’s the first time for them.
However, there is nothing as advanced or worrisome for anyone since everything is mentioned in detail for a newbie or expert person about using this platform.
None of the Personal Information or Credentials will ever be asked from you to provide when getting the Results for the giveaways.
Everything is Worked through a Script, which is created by JahaSoft LTD, a well-known Software Company and the creator of this website.
Whatever options or features you select for the online Giveaways Contest; the Script will work accordingly to provide you the Desired Results.
Hence, there would be fewer hassles situations for you to choose the Winner by yourself.
Meanwhile, the random Winner selection will never raise any issues of injustice as well.
Therefore, everything will remain as transparent and Worthy for the one who is Hosting the Giveaway.
Free Instagram Comment Picker Without Login:
Many of you might not want to Log-in to the Instagram Comment Picker platform to get the Giveaway Results. There would be several reasons that justify the whole situation. Hence, you would not either need to do it at all for any reason.
As long as the Comment-picker is concerned, you can install its extension on the Google Chrome Browser. After that, you can use the Instagram Comment Picker without providing any login Credentials. So everything will turn out to be as easier and simplified for you every time you get in with this Extension.
How to Use Instagram Comment Picker For Mobile Users?
Many of you don’t have PC services; therefore, you would be looking to use the Comment-picker platform to pick the comment for free from the Giveaway Post easily.
In that case, you can directly open the website on the Google Browser and log in.
Also Read: How to Turn Off AutoPlay Videos on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, Reddit, and More
For that, you can choose the Options of Log-In with Google or Facebook depending upon your needs.
After you do so, paste the link, and the platform will fetch out the data for you based on the functions or options you have selected.
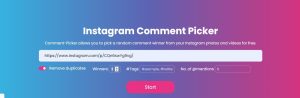
How to use Comment-Picker.com?
Comment-picker is not a heavy Tool that would make hurdles for you to use. Follow the below steps, and you can easily start Getting the details of winners for the Giveaways through the Comment sections.
Step 1: First of all, you need to get into the official website of Comment-picker.
Step 2: The second step is to paste the URL of the Instagram Giveaway Post onto the URL bar section available in the home. Remember, you can post both Videos and Photos of the Instagram Giveaway to get the results.
Step 3: The third step is to put the Filters in the Comment Picker. For that, it has no. of @mentions, Tags, Winners, and Remove duplicate. All of them have some purpose of usage.
Removing duplicates will erase all those peoples who are constantly commenting with the same ID. The winners will help you to select as many winners.
The Tags will curate only those people who have included the right ones.
In the last, the no mentions will be the people the contestants have mentioned as per the Rules.
Step 4: The fourth step will be to Click on the Start button, and it will automatically give you the Details of the Winners.

Why Use Comment-Picker Tool?
The Comment-picker is an easy-to-use tool website where you can easily restrict all those from the Instagram Giveaways who violate the Tools.
Moreover, as we have mentioned earlier, it has several features designed after many research processes. Hence, you will get the demanding results in return, which will be outstanding.
Apart from that, the creators of this platform are experts in IT Industry. Yes, Jahasoft LTD is the one who has created this Platform for the Social media Influencers of Instagram who find it hard to select the number of Winners from a Giveaway since there are hundreds of thousands of people who participate.
Also, it takes less time to curate the list of winners, which saves the whole time for you.