
Web Foundations
Introduction
The foundation of the web was laid around the 1960s in USA, when the ARPA (Advanced Research
Projects Agency – renamed as DARPA – Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency) researched into
a localized networking concept on how they can share text documents from one computer to another
The technology they researched was aimed at how these computers can communicate even if a portion of the phone network crashed during say a war or flood or any calamity When the then phone network was based on circuit switching technology, this research actually gave rise to the birth of packet switching in networks. The new model aligned well with the fact with that information was sent in bursts or packets at some time intervals
THE EVOLUTION OF THE WEB
It is reiterated that the web in its present state did not grow overnight, nor it designed formally as a roadmap. In fact one of the most critical success factors of the web can be attributed to the thought of independent innovations. According to this, smaller systems get architected and developed independent
of each other in possibly different environments. Suddenly, they come together and when merged, t
open to form interesting applications in entirely different ways. According to Tim Berners-Lee
following is an observation
Suppose someone had (and it was quite likely) invented a World Wide Web system somewhere
the same principles. Suppose they called it the Multi Media Mesh) and based it on Media Resources
Identifier, the Multi Media Transport Protocol, and a Multi Media Markup Language, After a few
years, the Web and the Mesh meet. What is the damage?
A PEEK INTO THE HISTORY OF THE WEB
The history goes back to the packet switching technology first used when two computers talked to
other, Multiple nodes operate independently thus reducing impact in case of point failures.
Thus TC’/IP was developed A few big companies like Cisco are specialized in networking technology
and is a big science by itself. The first generation of the web was in the form of private networks. The
networks were shared within the defense another set of networks (SURANET, etc.) was within the
university campus. Here are some trivia bit of information:
DARPA creates ARPANET – 1968
first set of nodes connecting universities among UCLA, Stanford, and University of Utah -1970
First E-Mail sent – 1972
Development on TCP/IP – 1973
USENET-decentralized news group
NSF creates CSFNET which is a 56 kbps network within institute
TCP/P made used in ARPANET
IPv4 formal introduction – 1980
IBM PC – 1981
DNS – 1983
Internet, www – 1992
1000s of new hosts added to internet 1994
The Federal Networking Council (FNC) defines the term ‘Internet’ – 1995

The growth from private to public networks gave rise to the Internet. According to FNC the Internet is
defined as follows:
Internet refers to the global information system that
(i) is logically linked together by a globally unique address space based on the Internet Protocol
(IP) or its subsequent extensions/follow-ones
(i) is able to support communications using the Transmission Control Protocol/internet Protocol
(TCP/TP) suite or its subsequent extensions/follow-ones, and/or other IP-compatible protocols
and
(ii) provides, uses or makes accessible, either publicly or privately, high level services layered on
the communications and related infrastructure described herein.
Thus the Internet is a network of networks, joining many computers together from different organizations, providing an infrastructure for various applications.
INTERNET APPLICATIONS
Internet is the platform for connecting computers together, but what can be achieved? Well, in short It is the world as the World Wide Web (WWW) is the most popular and widely used Internet based application. But there can be other uses as well like E-Mail, FTP, Bulletin boards, hyper text documents, etc.
The focus of the article will be the WWW, although other applications will be covered to the extent that is required to understand the context.
NETWORKS
A network can be considered as a series of computers connected together physically or virtually. The internet together a set of networks which are also called nodes, when they abstract a set of computers (or even other nodes) together A network can be referred to as a local area network (LAN) or a wide area network (WAN), or a metropolitan area network (MAN) depending on the range it spans, A LAN is normally confined to a limited geographic area, such as a building, and comprises from a few as three to as many as hundreds of computers. A WAN by contrast is a combination of multiple LANs that are geographically separate. The largest network of all is, of course, the Internet.
Packet switching technology allows multiple nodes to operate independently thus mitigation impacts in case of points of failures. This in turn gave rise to TCP (transmission control protocol). The first generation of the web using this was in the form of private networks. Private in the sense it was shared within the Defense services for example, or for that matter, within in a University
In parallel there was a revolution going on in personal computing Ever since IBM introduced the first
PC, The power of clients side computing became intense. Progress in chip design even exceeded Moore’s predictions about the power of processing. The PC became popular & personalized with laptops becoming commercially affordable to corporate as well as homes.
From Moore to Metcalf
As a result of the tremendous increase in processing power, the growth from private networks to
public networks was achieved. With that, the growth in internet became imminent. Literally, we
witnessed Moore’s law of computing in action and now, we are realizing Metcalf
communication networks getting true According to Metcalf’s theory, two communication devices (it is
not yet a network) can join to form one connection, whereas four of them can make 8 and sixteen
of them can make 120 connections. Obviously, these are more theoretical connections rather than
real useful ones but then Social networking will come into play to maximize the effectiveness of the connections.
By now, we have a few very big companies solely specialized in networking, like Cisco, Juniper
Networks, etc
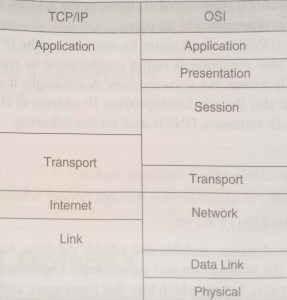
TCP/IP
Coming back to TCP/IP this deserves special mention since it is at the foundation of any computer
network. It evolved from ARPANET which is a WAN protocol Compared to the OSI model of seven
layers; TCP/IP has four layers, though not as rigid a layering.
The success of TCP/1P as the major protocol for the Internet is largely because of IP which enables
hosts to connect together geographically dispersed networks of computers irrespective of their size or
types of links The way in which this is done is through the concept of a host and a subnet. The IP protocol uses this concept. The Internet (IP) address is a means to uniquely identify a resource which could
desktop, printer, etc, on the Internet.
Internet Address Structure
The IP forms the basis of communicating data using packets. IP version 4 (IPv4) it’s the version that
is commonly used today, though IPv6 has been there for quite some time, standardized in 1998. IPv4
uses 32-bit notation which allows up to 232 unique addresses. The IPv6 uses 128 bit notation and offers
markedly more than what IPv4 offers but more importantly it addresses the requirements of subnet
routing prefixes within the address.
A 32-bit based address typically is represented as shown in the Address Structure figure. It consists of
sections with each section represented by an octet
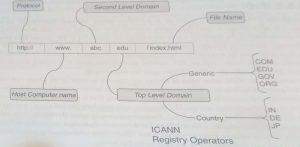
the domain name service (DNS) makes it easier for users to use the IP address. The unique logical
IP address representing the host computer is rather cumbersome to type in and remember, so it is
substituted by human friendly names like www.abc.com. Accordingly, it does Forward Lookup (from
Hostname to IP address) and also Reverse Lookup (from IP address to Hostname). DNS also enables
E-Mails to function properly. In summary, DNS is used for the following
IP name resolution
Hostname resolution, enabling use of consistent names
Internet domain support – to access servers through remote networks
E-Mail through outbound SMTP server
The DNS is viewed as a huge, dynamic, scalable and reliable database, but distributed globally there
is no one server that has all the information and rightly kept! Logically, it comprises three items
Namespace (which is the Domain), Servers which take that name space and Clients which seek clarifications within the name space.
Most top level domains (TLDs) with at least three characters are referred to as generic TLDs (gTLD).
The earliest ones created, which are still in use, are .com. gov, net, .org and .edu There were others like .aero, .muscum and .coop as also a set of unsponsored ones like .biz, .info, .name and .pro. The sponsored domains are represented by a specialized community.
In fact, the addresses, starting from any of these TLD, are similar to the physical address structure
that we commonly find for residences. As we go down from the TLD (which could be the equivalent of
a country in the residential address), it converges each level to a more narrow scope. It goes on until it
finds the smallest entity. In the Internet this entity is referred by a resource (as the A element).
IPv6
Though the 1Pv4 system can support up to 4.3 billion unique addresses theoretically, on its address
space it is not sufficient to meet the growing numbers of devices and users that are required. Now, we
have almost reached the threshold where more things are connected to the Internet than people. Cisco
predicts the number of Internet-connected things will reach 50 billion by 2020, which will equate to
more than six devices for every person on Earth. Already, the numbers of possible devices that have been
connected are quite many – laptops, PCs mobiles, Smartphone’s, tablet PCs, gaming devices, TV, etc. By
February 2011, officially, all of IPv4 address space has been used up
The trend is that many more types of devices are expected to come in the future that will be web-
connected and they
near field communications (NFC), sensor networks, etc, that have the ability
collect, transmit and analyze information. The point regarding IPv4 is that these devices have contributed to the depletion of IP addresses very quickly. Moreover, companies have blocked a larger number of address spaces than what they actually require or use. Furthermore security needs also require to be enhanced. All of these reasons justify the need towards IPv6. For the records, there was a move towards IPv5, but since the additional features were far fewer to warrant a new release, those were merged as part of IPv6 itself.
The advantage and features of IPv6 are summarized as below:-
. Additional address space: IPv6 is based on 128 bits thus allowing for up to 2128 unique devices.
This is the single most important advantage of IPv6. It also obviates the need for techniques like
NAT which is used with IPv4.
Telnet
Telnet (Which stands for terminal network) allows a user to login to a serve and work off a window in the client’s machine. As in FTP, there are two parts to it – a client and a serve.
E-Mail Related Protocols
People need to communicate with one another through some formal means, including as much as to
conduct business. Earlier, during the mainframe days, communication was done through connected systems one-to-one. As systems became interconnected, it was required to communicate irrespective the underlying operating system. So, standard protocols began to emerge for E-Mail. There are two main protocol standards used for E-Mail over the Internet and it is important to make a mention of them POP and SMTP
SMTP
SMTP which stands for simple mail transfer protocol, it is a text-based protocol. It
works across TCP/IP from ports 25 or 587. It operates as the application layer, defining the transport
as opposed to the mail content. Handling mails can again be thought of as a client-server system. The
mail server uses SMTP to send and receive messages. The client uses SMTP to send mails. The mail
client could be Microsoft Outlook, Notes, or any such software (including a browser) that are commonly
familiar. For receiving, typically the client uses the POP or IMAP protocol over the web. The mail client
could also belong to one of the proprietary tools like I
office protocol in this context (not to be confused with point of presence, which denotes an access point
Lotus or Microsoft Outlook. POP stands for post office protocol in this context did not confused with the point of presence which denotes an access point
to an Internet ISP).
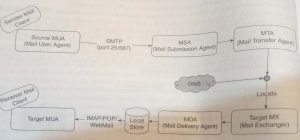
The overall flow of mail from the sender (Source) to the receiver (target) is shown. The idea is not
e reader understand easily but also get used to a few terms that are used in the process. It
necessary to know the details of each step for a web programmer, as each step is detailed in itself
under networking Notice that the client part on the receiving end can access mails through
either IMAP or POP (or POP3 representing the version of POP) or Webmail
The server is (required to be) online all the time for receiving messages and storing in a local store
However this need not be the case for the client. As per POR the recipient palls his/her mails into a
personal hard-disk, so that the user need not be online all the time for checking messages It is similar to
the process of chewing the-cud in animals, wherein messages are downloaded at suitable intervals when online, and then each of these can be read and acted upon by the recipient offline
IMAP
Developed by Stanford University, IMAP stands for internet message access protocol.
it is meant for accessing E-Mails through the internet. It was designed to work even on low bandwidth
speeds, by downloading only the header – the user has the option to download in full only those messages those are required. The advantage is that unimportant messages like spam or anonymous not be downloaded
Advanced versions of IMAP (like IMAP4) has facilities to search through the body of mail messages
for keywords which will further help in filtering messages
MIME
Traditionally, E-Mail handling was designed based on text types of files and hence
were ASCIl-based. However, it needed enhancements when binary messages needed to be transmitted,
since they came about when mails were used in the context of business. It was then that standards like
MIME were introduced. The purpose was to handle additional file types (in E Mail) without having
to change the then existing (E-Mail) infrastructure It started as a means for encoding binary files for
transfer through SMTP However, usage of MIME has now grown into a generic content type to be used
in communication protocols like HTTP It is, in fact, designed to be extensible
MIME stands for multipurpose internet mail extensions, its expansion still reflects just the older
meaning, though
IANA defines the standard MIME file types. This is manifested in the content-type, as part of the
HTTP header. The standard types are mentioned below.
• Application
• Audio
• Example
• Image
• Message
• Model
• Multipart
• Text
• Video
There are subtypes under each of the above types (except example). For example, text/html identifies an HTML file. Other examples include image/jpeg, application/xml, text/xml, etc.
HTTP
Hyper Text Transfer protocol (HTTP) is a protocol that utilizes TCP to transfer information between computers connected on the web – this includes web servers and clients as well. This is the communication mechanism that browsers use to exchange data from clients to servers. The client makes an HTTP request to a web server using web browser. And the server sends the requested information (website) to the client. The standard port used for connection between the client and server is 80.
Talking about the connections. These are the most important features to note, which is unique to this protocol. They are mentioned below.
Awesome Topic its really helpful
Sir First of all hatsoff of Ur hardwork…I wanna be a ethical hacker like U and I am searching all the things for this..but no one really can take classes deeply like U frm basics thank u sir for doing this and I have to doubt in my carrier I don’t know where to start?
1.What I am studied for CEH? Is there enough to study the books of CEHv6 to CEHv9 for CEH
2.Where the xams are conducted, is there any website for getting these information?
Can u please elaborate what are the steps we are attempted for CEH
Thank U again
Thank you brother.
Well I recommend you to Read Latest Version of CEHv9 rather CEHv6 is bit older. CEHv9 Sybex Book is one of the perfect book to start or you can go for Video Tutorials from CBT Nuggets CEHv9 he is the best instructor out there for CEHv9 Video Lectures, You can find those lectures with Book here in this blog just Search and Get and Download them for free. And then start learning from basics to an advanced level.